Type: Polymodal (interneuron, motor neuron)
Connectivity:
- In MoW: AVL
- In WormWiring: AVL, AVLm
- In Nemanode: AVL
In Wormbase: AVL
Lineage: AB prpappaap
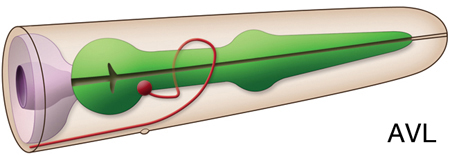
Location: Ventral ganglion in head
Description: An excitatory motor neuron for enteric muscles as well as a ring and ventral cord interneuron. In males, makes gap junctions with PDB, has a few synapses onto gonad and ventral body wall muscles (Jarrell et al., 2012).
Neurotransmitter/ Neuropeptide:
-
GABA
(Eastman et al., 1999)
|

|